Jithin B.P.
Jithin B.P.


 Jithin B.P.
Jithin B.P.
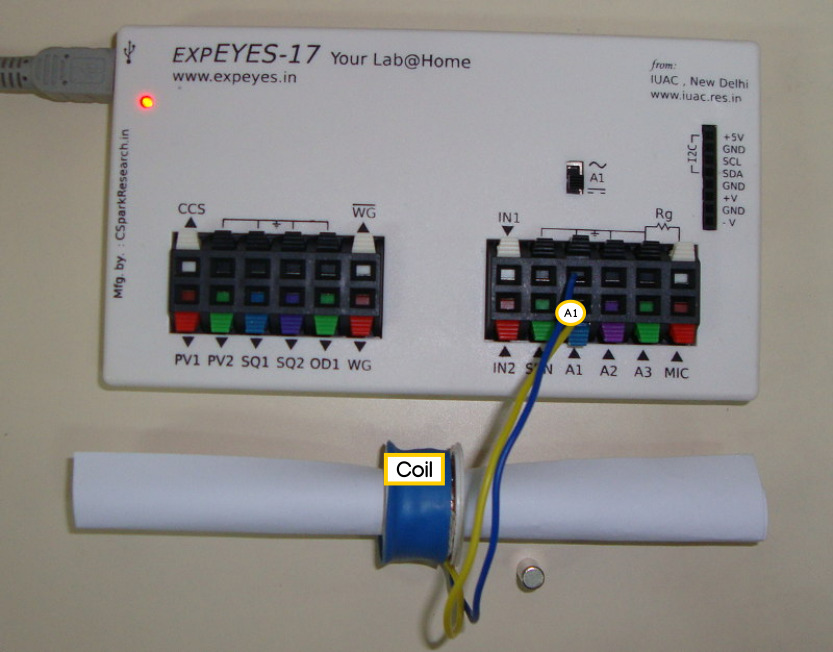
A coil is connected between the oscilloscope input A1, and GND. The oscilloscope software then waits for a signal to capture and plot.
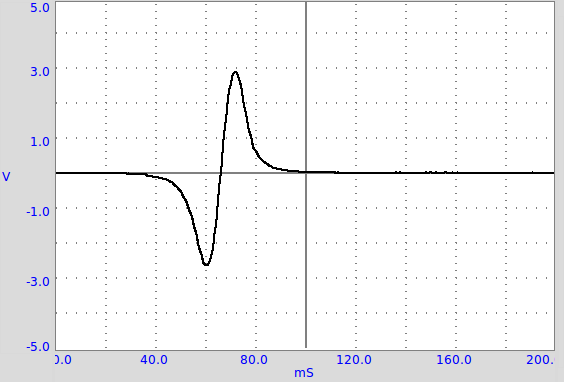
A magnet is dropped through the solenoid, with the help of a paper roll for guiding it properly, and the induced voltage is observed.

While the magnet approaches the coil, the rate of change of flux also increases. So you see the EMF go up / down depending on the direction of the magnet.
Once the magnet’s center crosses the center of the coil, the rate of change in flux changes polarity since the magnet is now exiting the coil, and as a result, the EMF also changes polarity.
You will also notice that the absolute peak value EMF as the magnet exits is more than that when it was entering. This is because the magnet is accelerating due to gravity, and has a slightly faster velocity while leaving, and therefore, a larger EMF is induced.