 Jithin B.P.
Jithin B.P.

 Jithin B.P.
Jithin B.P.
The boundary layer between two thin films of a semiconducting material with Positive type and Negative type doping is referred to as a P-N junction, and these are one of the fundamental building blocks of electronics. These junctions exhibit various properties that have given them a rather indispensable status in modern day electronics.
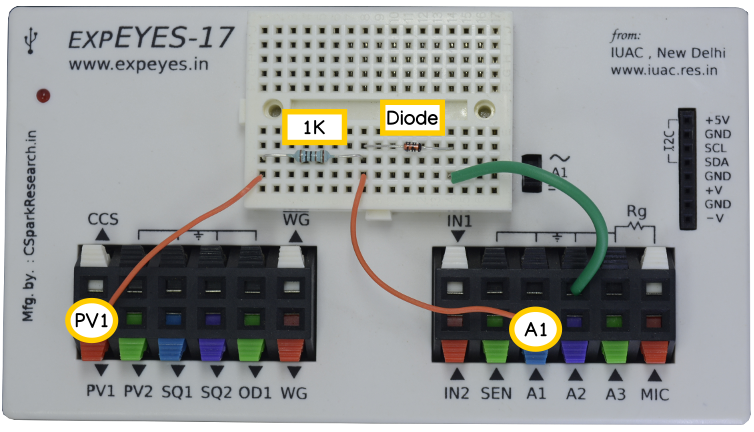
The schematic is wired as shown in the diagram below. The voltage across the diode is measured on A1. The anode of the diode is connected to PV1, through a 1k resistor. Voltage at PV1 is incremented in steps and at each point the voltage across the diode is measured. The current is calculated from i = (PV1-A1)/R. The diode used is 1N4148, silicon diode.
The various measurement tools of ExpEYES enables us to understand these devices, and in this blog post we shall look at how a diode behaves at various bias voltages.
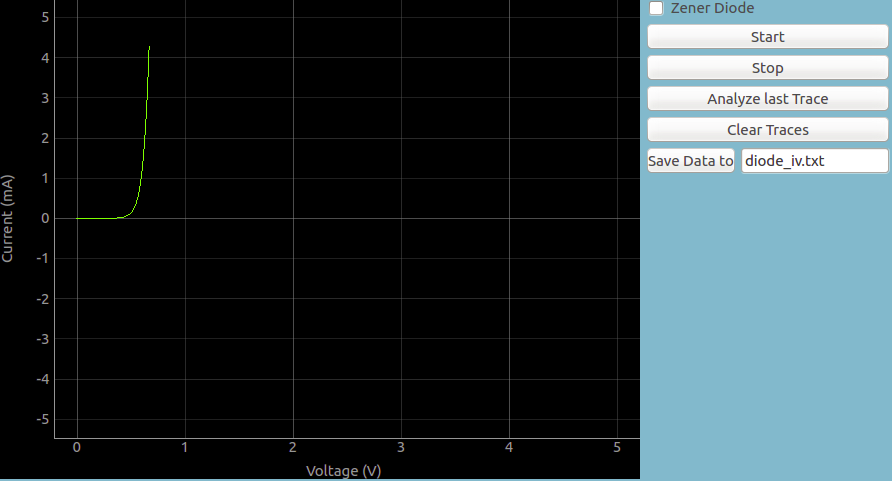
An ideal diode has zero resistance in the forward direction, but in practice, diodes only start conducting in the forward direction after a certain threshold potential difference is present.
This voltage, also known as the knee voltage or barrier potential, depends on the band gap of the diode, and we shall measure it to determine how the electrical properties affect the externally visible physical properties of the diode(in case of LEDs).
A programmable voltage output of ExpEYES (PV1) is increased in small steps starting from 0 Volts, and a voltmeter input (A1) is be used to determine the point when the diode starts conducting.
The presence of a known resistor between PV1 and A1 acts as a current limiter, and also enables us to calculate the current flow using the Ohm’s law. I = (PV1-A1)/1000 , where 1000 Ohms is the value of the resistor used.

Zener diodes are a special category of diodes that also conduct electricity in the the reverse direction once a certain threshold has been crossed, breakdown voltages such as 3.3V , 5.6V , 6.8V etc are commercially available. A 3.3V Zener is supplied with the ExpEYES kit along with regular 4148 diodes. The I-V characteristics of a 3.3V zener diode can been measured with expeyes by selecting the zener option . In this mode, the voltage is swept from -5 V onwards.