 Jithin B.P.
Jithin B.P.

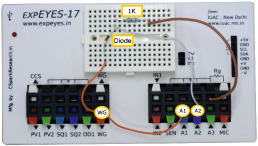
 Jithin B.P.
Jithin B.P.
Half wave rectifiers cut off one half of a waveform, and further filtering with a capacitor enables generation of a DC signal from an AC signal.
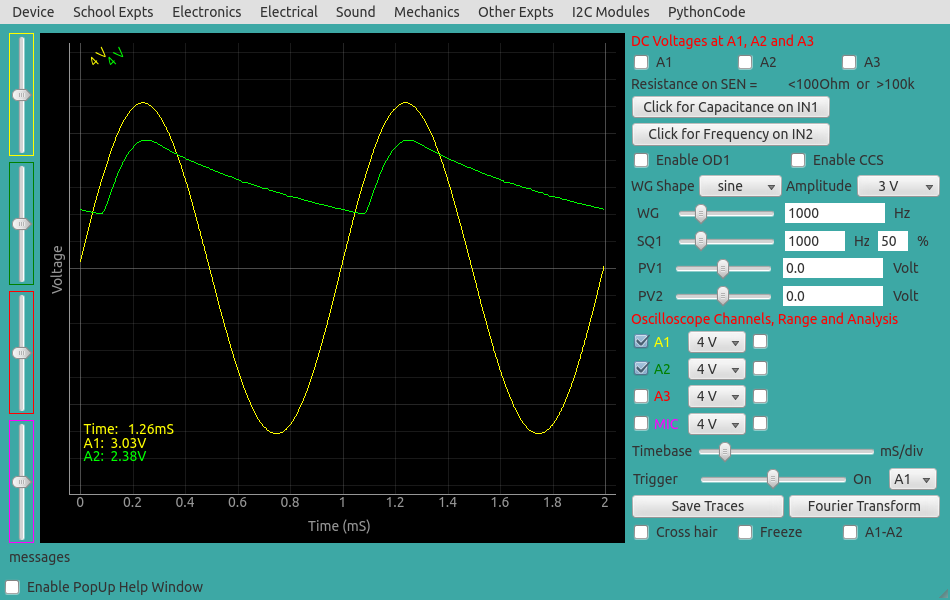
The waveform generator WG is set to give a sine wave of 1kHz. It is monitored by oscilloscope channel A1. The signal after the diode is monitored by A2. The observed waveform will be a bit noisy without the load resistor, connecting a 1k resistor gives a clean rectified waveform. The voltage drop across the diode is clearly visible. Connect different values of capacitors to view the filtering effect.
Screen shot of the oscilloscope program showing input and output of half wave rectifier. 1N4148 diode at 1000Hz and 1kOhm load resistor.
In case you hadn’t noticed, the output waveform has a lower peak voltage than the input. This is a result of the barrier potential
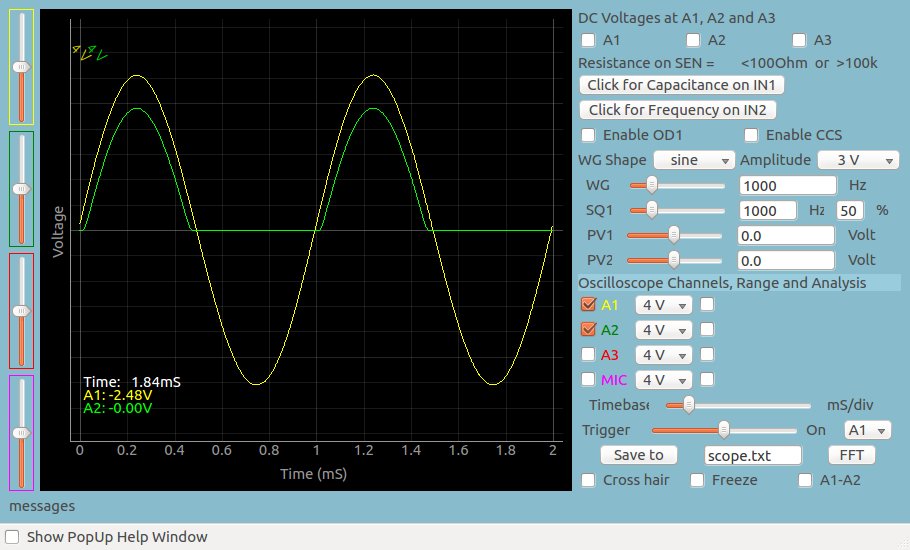
The output after adding a 1uF capacitor for filtering is shown below. With increasing RC value, the ripple reduces.

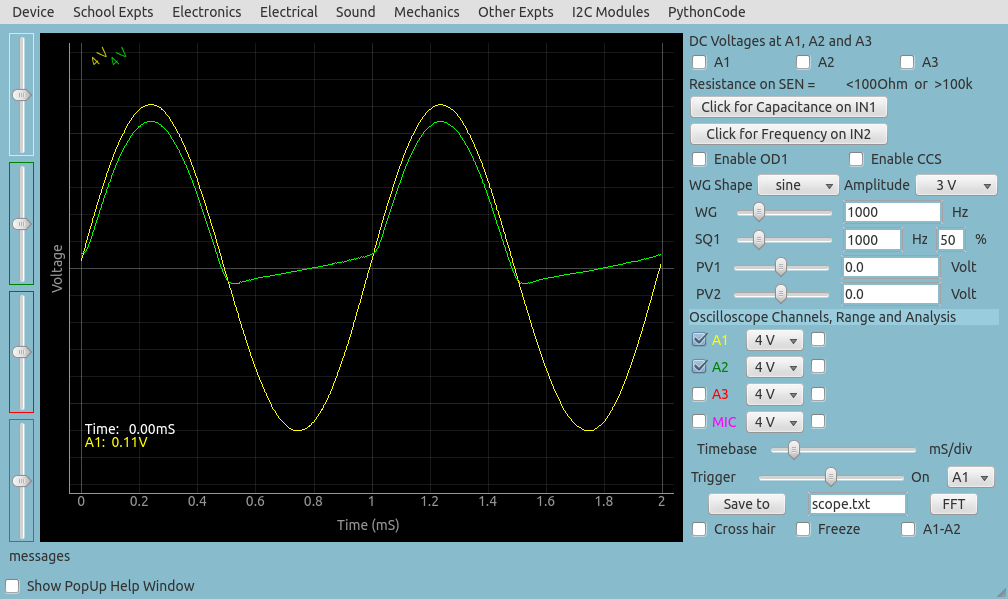
Every diode has a junction capacitance that acts like a capacitance connected in parallel to the ideal PN junction. Junction capacitance of 1N4148 is only 4pF but 1N4007 has a junction capacitance of 20pF. The rectified output, without external load resistor, for 1N4007 is shown below. The 1MOhm input impedance of channel A2 will be always present.
This experiment can also be done by running this Python Code. The output of the program is shown below.
#Python code to study a halfware rectifier
import eyes17.eyes
p = eyes17.eyes.open()
from pylab import *
p.set_sine(200)
t,v, tt,vv = p.capture2(500, 20) # captures A1 and A2
xlabel('Time(mS)')
ylabel('Voltage(V)')
plot([0,10], [0,0], 'black')
ylim([-4,4])
plot(t,v,linewidth = 2, color = 'blue')
plot(tt, vv, linewidth = 2, color = 'red')
show()
